CityGML Schema Options
If set to Yes (the recommended setting), this parameter reads the core CityGML schema files as well as the schema files specified in either xsi:schemaLocation attribute in the XML document or ADE_XSD_DOC directive to determine the feature types and feature attributes of the dataset.
It is recommended that this parameter be set to Yes for new workspaces and mapping files reading CityGML 1.0, 1.1 and various ADE datasets.
Note: You can duplicate the CityGML reader’s behavior for workspaces older than FME 2012 by setting this parameter to No. Please note that setting this parameter to Yes is not backward compatible if the dataset contains NoiseADE data.
This parameter can be used only if the Reader Driven by CityGML Schema parameter is set to Yes. The schema files specified in this directive will override those specified in xsi:schemaLocation attribute in the XML document.
Determines whether the reader should validate the specified dataset file.
This parameter can be used to tell the reader to ignore the schema files that are specified in the xsi:schemaLocation attribute of the root element in the dataset. This is particularly useful if the file locations specified in xsi:schemaLocation are not valid file paths.
FME feature type names may include the XML Namespace prefixes used in the GML application schema. The prefix will be separated from the names by an underscore.
Setting this parameter is necessary when a GML dataset contains feature types with the same name in different namespaces.
By default, the prefixes are not added to the feature type names.
This parameter is applicable only in scenarios when the reader dataset field is empty.
For example, the Reader dataset might not yet exist when the CityGML reader is used to "Import Feature Types" to the CityGML writer.
Note: This parameter does not override the Additional ADE Schema File(s) parameter.
Limits the number of FME nested attributes that an XML element and its children are mapped into. If the specified limit is reached, then the XML element is simply mapped into an XML fragment.
Default value: 400
FME Schema Options
If selected, only the feature types found in the dataset will be created. Otherwise, all feature types that are found in CityGML core and additional schema files (as specified in Additional ADE Schema File(s) or xsi:schemaLocation) will be created.
Include Generic Attributes as Feature Types: If selected, an extra GenericAttribute feature type will be created to hold all the features created from generic attribute elements (stringAttribute, intAttribute, doubleAttribute and so on).
Include X3DMaterial, ParameterizedTexture and GeoreferencedTexture as Feature Types: If selected, feature types for X3DMaterial, ParameterizedTexture and GeoreferencedTexture elements will be created.
Include Generic Attributes in FME Schema: Regardless of the value specified here, generic attribute will always be read as FME attributes. If this option is selected, those attributes will also show up in FME schema.
CityGML Options
If Yes, the reader adds xlink_href geometry Traits to the FME geometries that were instantiated from GML xlink:href reference geometries.
In addition, if the xlink:href geometry reference is from a base surface of a GML OrientableSurface that needs to be reversed, the reader also adds a gml_geometry_reversed boolean trait set to Yes to the FME geometry.
SRS Parameters
Overrides the axis order when reading coordinate tuples in a CityGML <pos> or <posList> element. Valid values are "1,2", "2,1", “1,2,3” and “2,1,3”.
This directive should only be set to YES if the source datasets have texture coordinates and were created by the CityGML writer in FME versions prior to FME 2012. Otherwise, it should be set to NO.
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
Use Search Envelope
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned.
If all four coordinates of the search envelope are specified as 0, the search envelope will be disabled.
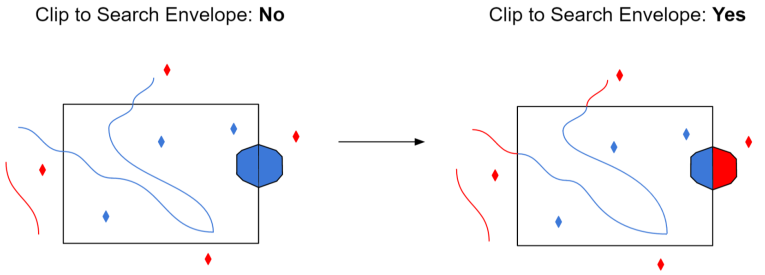
When selected, this parameter removes any portions of imported features being read that are outside the Search Envelope.
The example below illustrates the results of the Search Envelope when Clip to Search Envelope is not selected (set to No) and when it is selected (set to Yes).
- No: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
- Yes: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read. The underlying function for the Clip to Search Envelope function is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is selected, a clipping operation is also performed in addition to the intersection.
Use Network Authentication
This parameter is always visible in some formats, and visible in other formats only when the dataset is a URL.
Specify the authentication method to use when accessing a password-protected server.
- Basic: (default) Basic access authentication is designed to allow a client to provide credentials to a server on the assumption that the connection between them is trusted and secure. Note that any credentials passed from client to server can be easily intercepted through an insecure connection.
- Digest: Digest authentication is one of the agreed-upon methods a web server can use to negotiate credentials, such as username or password, with a user's web browser.
- NTLM: A challenge-response protocol that is used to provide compatibility with versions of Windows earlier than the Windows 2000 operating systems.
- Web Connection: Web connections provide a convenient and secure way to store and reuse previously established connection parameters. See Web Connection below.
- Single Sign-on: FME will use the credentials of the current user to authenticate the HTTP request. This authentication method currently works only on the Windows operating system.
Note: To access datasets using a proxy server, use the Network tools in FME Options. From the Workbench menu, select Tools > FME Options > Network. For more information, see "Network Proxy" in the FME Workbench Help.