Locating Transformers
FME contains hundreds of transformers, and it can sometimes be challenging to locate the ones you need. There are several ways to source the proper transformer:
Click the undock button  to separate the pane from the main Workbench interface.
to separate the pane from the main Workbench interface.
Transformer Categories
Transformer categories are a good starting point from which to explore the Transformer Gallery. Transformers are grouped in categories applicable to their associated functionality.
- 3D: Create and modify 3D surface and solid geometries.
- Calculators: Calculate a value and supply it as a new attribute.
- Collectors: Use or create collections or groups of features.
- Coordinate Systems: Modify coordinate systems and reprojection.
- Database: Interact with external databases.
- Filters: Split and reroute data
- Geometric Operators: Process feature geometry.
- Infrastructure: Provide interaction with the underlying FME translation engine facilities. These include functionality to log features, set feature colors, create individual features and grids of features from nothing, and inspect features with the FME Data Inspector.
- JSON: Query, update, and create JSON data.
- KML: Manipulate feature geometry and/or attributes for output using the OGCKML Writer.
- Linear Referencing: Work with linear referencing data structures on FME features.
- Lists: Work with list attributes.
- Manipulators: Operate on individual features (the opposite of Collectors).
- MapText: Create text labels for features. These transformers are built using technology developed by MapText, Inc.. The MapTextLabeller is extra-cost.
- MRF: Repair geometry, particularly during data migration from CAD to GIS. They are built upon an integration of MRF Geosystems Corporation's cleaning technology into FME. These transformers are all extra-cost.
- Network: Operate on linear features that are connected in a network, performing operations such as priority calculation and orientation correction.
- Point Cloud: Create, use, and output point cloud features. They operate only on data consisting of point clouds.
- Rasters: Create, use, and output rasters. They operate on data consisting of a regularly spaced grid of values.
- Strings: Create, modify and delete string (character) attributes.
- Stylers: Prepare features for output to particular formats by providing a convenient interface for setting color and other display characteristics
- Surfaces: Create, use, and output surfaces.
- Web Services: Access web services via the HTTP protocol.
- Workflow: Run workspaces either locally or on an FME server.
- XML: Work with XML data by mapping XML elements into FME features, using stylesheets to convert XML documents, and query collections of XML data.
You can create your own folders to store any transformers that you create. These folders are saved as an external definition, so you can also share them with other users. In the example shown above, the Cities folder contains custom transformers.
Transformer Names and Descriptions
You can search the gallery for both transformer names and descriptions.
Enter a keyword in the Search field. The keyword can be a partial transformer name, or one or more keywords that describe its function.
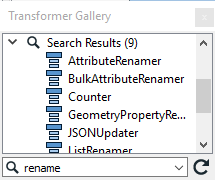
Workbench displays a Search Results node that contains a list of transformers whose name or descriptions contain the matching keyword.
Using Quick Add
Quick Add is the easiest way to add transformers to the workspace.