Database Connection
This is the ODBC data source name. When you enter the Database in the Input Dataset field, the Database field will be automatically populated in the Parameters box.
Enter the username and password to access the database, user account, or wherever authentication is required.
The time (seconds) after which to terminate a query to the database if it has not yet returned a connection/result.
If it is set to 0, there is no timeout. The default is 30.
Constraints
After you have completely specified the database connection, click the Browse button to select tables to import. A connection window appears while the system reads a table from the database.
Once the table list appears, you can select one or more tables, and then click OK to dismiss the window. The table name(s) will appear in the table list field in the Reader Parameters box.
An SQL WHERE clause can be applied to each table’s columns, to constrain the attributes of the layers selected in the layer list (for example, NUMLANES=2).
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario where you have multiple feature types, it is convenient to expose additional attributes using this one parameter. For example, if you have ten feature types and want to expose the same attribute in each one, it is easier to define it once than it is to set each feature type individually in the workspace.
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned.
If all four coordinates of the search envelope are specified as 0, the search envelope will be disabled.
When selected, this parameter removes any portions of imported features being read that are outside the Search Envelope.
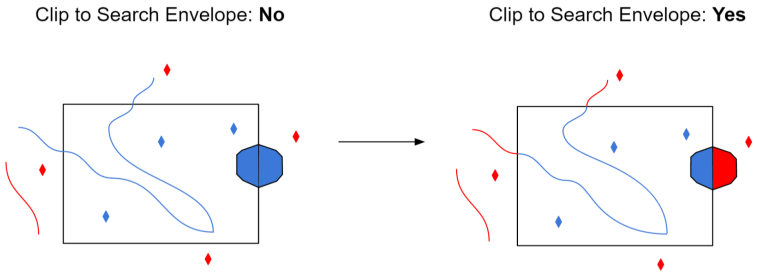
The example below illustrates the results of the Search Envelope when Clip to Search Envelope is not selected (set to No) and when it is selected (set to Yes).
- No: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
- Yes: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read. The underlying function for the Clip to Search Envelope function is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is selected, a clipping operation is also performed in addition to the intersection.
Advanced
You may want to execute some ad-hoc SQL prior to reading or writing a table. For example, it may be necessary to ensure that a view exists prior to attempting to read from it.
Multiple SQL commands can be delimited by a character specified using the FME_SQL_DELIMITER keyword, embedded at the beginning of the SQL block. The single character following this keyword will be used to split the SQL, which will then be sent to the database for execution.
Note: Include a space before the character.
For example:
FME_SQL_DELIMITER ;
DELETE FROM instructors;
DELETE FROM people WHERE LastName='Doe' AND FirstName='John'
Multiple delimiters are not allowed and the delimiter character will be stripped before being sent to the database.
Any errors occurring during the execution of these SQL statements will normally terminate the reader with an error. If the specified statement is preceded by a hyphen (“-”), such errors are ignored.
You may want to execute some ad-hoc SQL after reading or writing a set of tables. For example, it may be necessary to clean up a temporary view after writing to the database.
Multiple SQL commands can be delimited by a character specified using the FME_SQL_DELIMITER directive, embedded at the beginning of the SQL block. The single character following this directive will be used to split the SQL, which will then be sent to the database for execution.
Note: Include a space before the character.
For example:
FME_SQL_DELIMITER ; DELETE FROM instructors; DELETE FROM people WHERE LastName='Doe' AND FirstName='John'
Multiple delimiters are not allowed and the delimiter character will be stripped before being sent to the database.
Any errors occurring during the execution of these SQL statements will normally terminate the reader with an error. If the specified statement is preceded by a hyphen (“-”), such errors are ignored.