Feature Properties
Specifies whether predefined GML feature properties, which include fid, name, and description, should be read.
This parameter specifies whether the GML geometric properties should be represented as attributes in the FME feature type definitions.
In FME data features, the GML geometric properties are represented as a single named geometry – or, if multiple geometries are present, as an aggregate geometry with multiple named geometry components. The name and the position for these geometric elements can also be controlled through the GML Writer: User Attributes
- If this parameter is checked (which is the default), then the feature type definitions will contain the geometry names as attributes, and their type is set to xml_geometry. If an attribute X has its type set to xml_geometry, this attribute X becomes a placeholder in the feature type definition. It is a placeholder because actual data features for the feature type definitions will not have this attribute; instead, the data features will have a geometry named “X”.
- If this parameter is unchecked, then the feature type definition will not contain geometry names.
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario where you have multiple feature types, it is convenient to expose additional attributes using this one parameter. For example, if you have ten feature types and want to expose the same attribute in each one, it is easier to define it once than it is to set each feature type individually in the workspace.
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned.
If all four coordinates of the search envelope are specified as 0, the search envelope will be disabled.
When selected, this parameter removes any portions of imported features being read that are outside the Search Envelope.
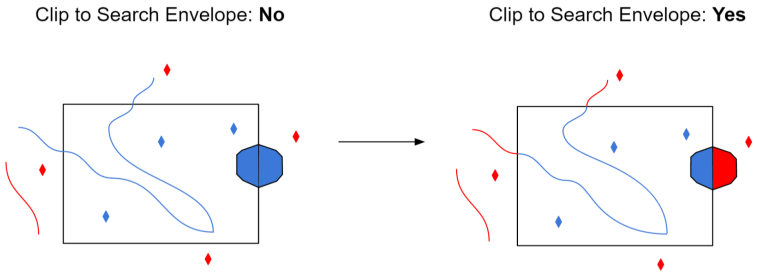
The example below illustrates the results of the Search Envelope when Clip to Search Envelope is not selected (set to No) and when it is selected (set to Yes).
- No: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
- Yes: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read. The underlying function for the Clip to Search Envelope function is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is selected, a clipping operation is also performed in addition to the intersection.