It’s assumed that SQL Server has been installed.
One notation used is <FMEServerDir>, which is the installation directory of FME Server. In Windows, this is typically C:\Program Files\FMEServer.
SQL scripts are provided to help with SQL Server database configuration. These SQL scripts are located in the <FMEServerDir>\Server\database\sqlserver\ directory of the machine on which the FME Server core was installed (not the machine on which the database is installed).
If you are upgrading, you should back up any job history you want to keep.
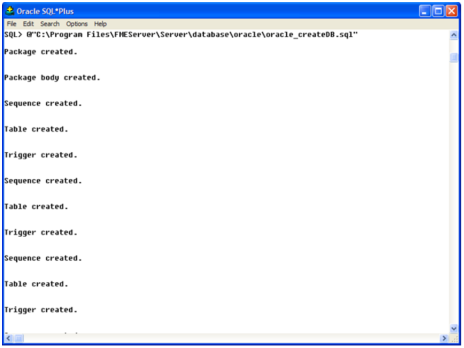
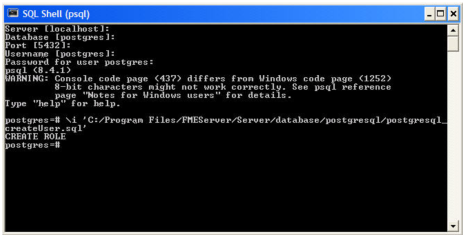
The SQLServer_createDB.sql script creates the required FME Server tables.
- Install Microsoft SQL Server if you haven’t already.
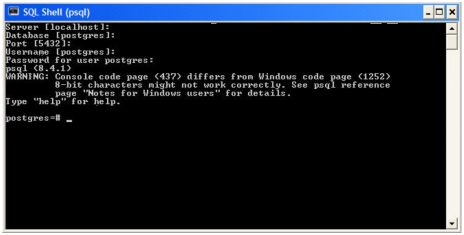
- Open the SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the SQL Server database engine.
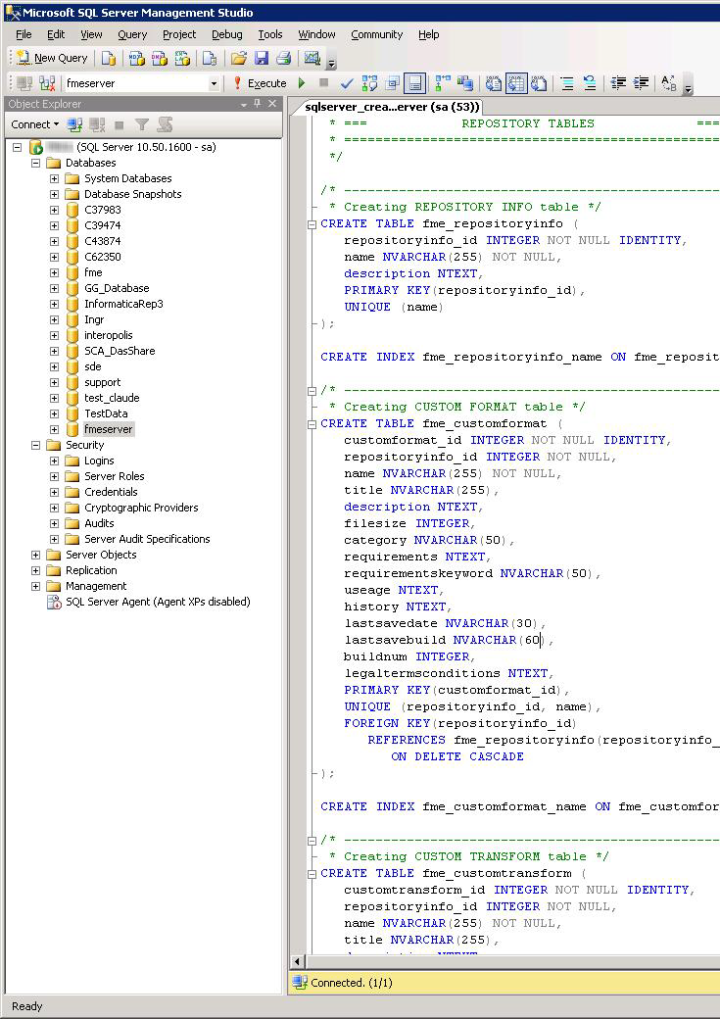
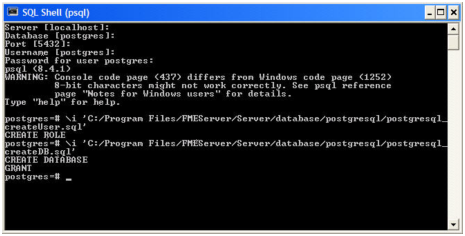
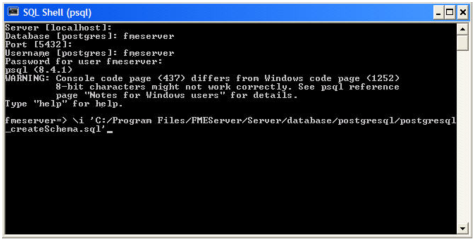
- Open sqlserver_createDB.sql and run the script against the fmeserver database, as shown below:
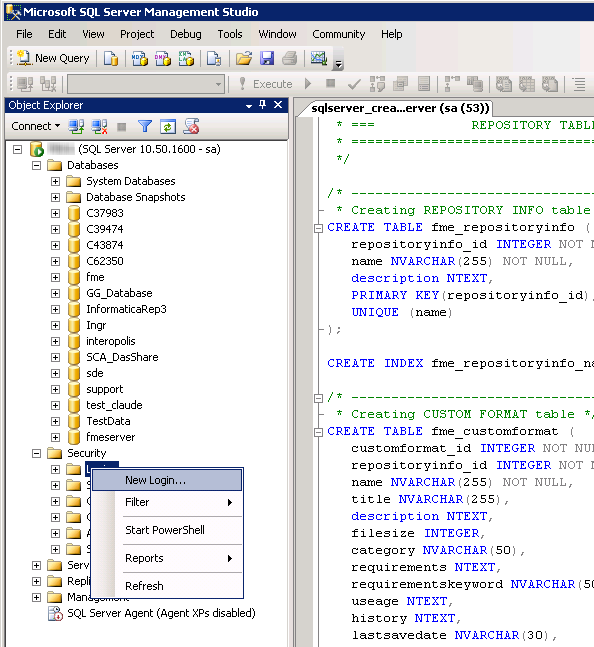
- On the Object Explorer pane, expand the Security folder, right-click Login, and then select New Login:
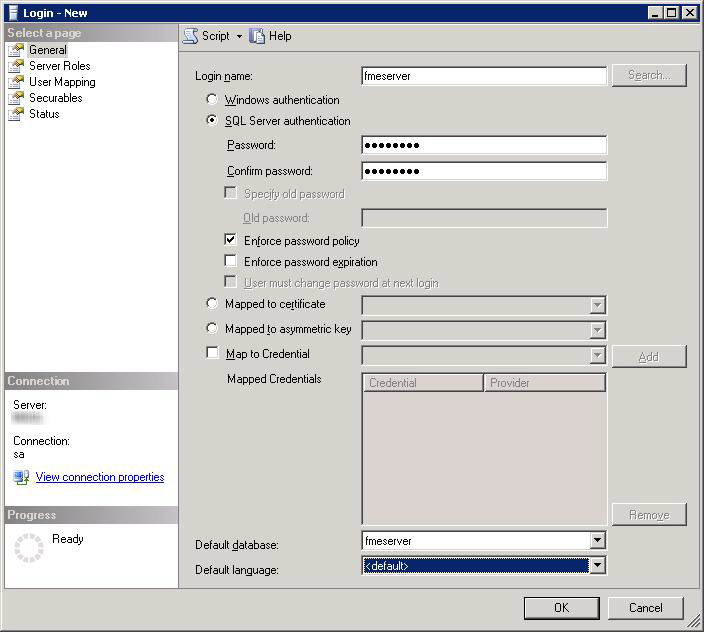
- On the Login – New page, click General to open the page shown in the example below.
- At the Login name field, enter fmeserver.
- Make sure the option button is active for SQL Server authentication.
- In the Password field enter the password of your choice, and in the Confirm password field enter the same password again.
- Make sure the Enforce password policy is active. If not, click the checkbox to activate it.
- If required, click the checkbox for Enforce password expiration to clear it.
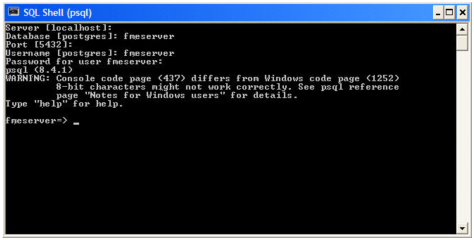
- At the Default database field enter fmeserver.
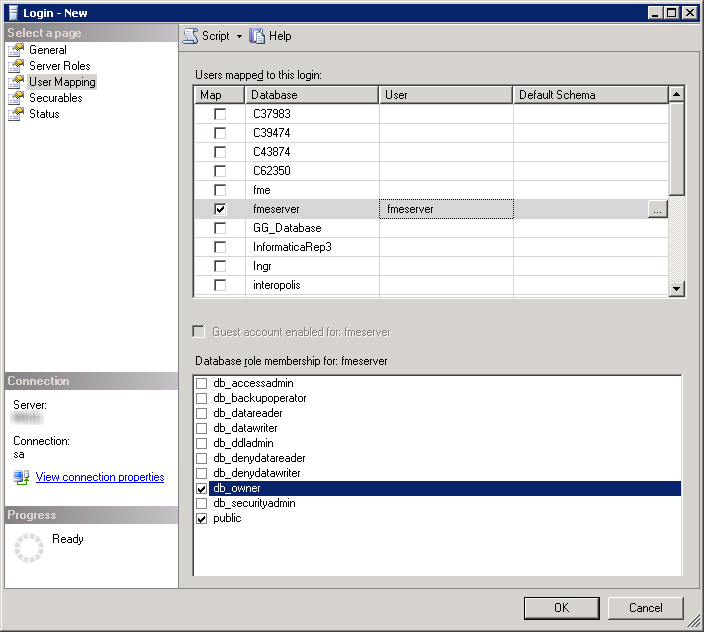
- On the same Login – New page, click User Mapping to open the page shown in the next figure.
- At the Users mapped to this login location, in the Map column click the checkbox to activate it and map the login name to the fmeserver database.
- At the Database role membership for location, notice that the fmeserver database is specified and check db_owner to assign that role to this database.
- Click OK to close this page.