Dissolves area features by removing common boundaries to create larger areas. Input attributes may be accumulated.
Input Ports
- This transformer accepts two-dimensional polygonal features, including donuts. These polygonal features are broadly referred to as polygons.
- Aggregate input will be deaggregated by the transformer. Attributes on the aggregate feature will be propagated to its parts.
Tip: If part-specific attributes, such as areas, need to be computed and preserved, please deaggregate before dissolving.
Because aggregates are deaggregated inside the Dissolver, it is possible that the number of output features will exceed the number of input features.
- Dissolved polygons are formed when shared edges and interior edges between adjacent polygons are removed.
Output
Dissolved polygon features with specified attributes.
Geometries and attributes that are left over after dissolving.
If the fme_remnant_type is INTERIOR_LINE, this remnant is a linear feature that represents the portions of the input polygons which were not part of the output dissolved polygon because the linear feature was either collinear with another feature, or was inside an overlapping region.
If the fme_remnant_type is UNUSED_DATA, this remnant is a feature that contains the remaining input data that was not part of the dissolved output. If the remnant feature has a geometry, this geometry was not used in the output. If the remnant feature does not have a geometry, this feature contains the attributes that were not used in the output.
Non-polygonal features are output via this port.
Parameters
Transformer
The input polygonal features may be partitioned into groups for dissolving by using the Group By parameter. If this parameter is not specified, then all input features are processed together. The Group By parameter enables a single factory to dissolve several sets of potentially overlapping polygons.
Process At End (Blocking): This is the default behavior. Processing will only occur in this transformer once all input is present.
Process When Group Changes (Advanced): This transformer will process input groups in order. Changes of the value of the Group By parameter on the input stream will trigger processing on the currently accumulating group. This may improve overall speed (particularly with multiple, equally-sized groups), but could cause undesired behavior if input groups are not truly ordered.
There are two typical reasons for using Process When Group Changes (Advanced) . The first is incoming data that is intended to be processed in groups (and is already so ordered). In this case, the structure dictates Group By usage - not performance considerations.
The second possible reason is potential performance gains.
Performance gains are most likely when the data is already sorted (or read using a SQL ORDER BY statement) since less work is required of FME. If the data needs ordering, it can be sorted in the workspace (though the added processing overhead may negate any gains).
Sorting becomes more difficult according to the number of data streams. Multiple streams of data could be almost impossible to sort into the correct order, since all features matching a Group By value need to arrive before any features (of any feature type or dataset) belonging to the next group. In this case, using Group By with Process At End (Blocking) may be the equivalent and simpler approach.
Note: Multiple feature types and features from multiple datasets will not generally naturally occur in the correct order.
As with many scenarios, testing different approaches in your workspace with your data is the only definitive way to identify performance gains.
Parameters
The minimum distance between geometries in 2D before they are considered equal, in ground units. If the tolerance is None, the geometries must be exactly identical to be considered equal. If the tolerance is Automatic, a tolerance will be automatically computed based on the location of the input geometries. Additionally, a custom tolerance may be used.
When viewed in 2D (ignoring Z), a path (which may define the border of a polygon) may appear to be closed as shown in the left figure below. This same path, when viewed in 3D, may appear to be open as shown in the right figure below.
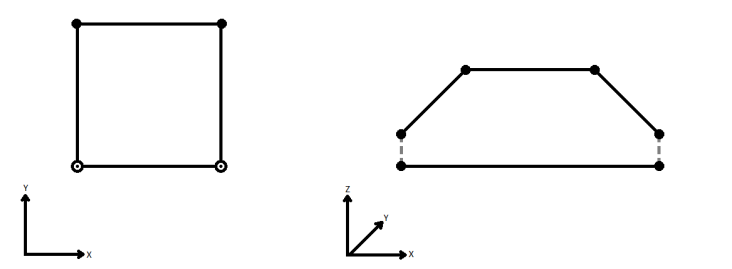
To specify how (and if) paths should be closed in 3D, select one of the listed modes.
| Mode | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Extend | The Curve is extended so that all vertices are left at their original location. |
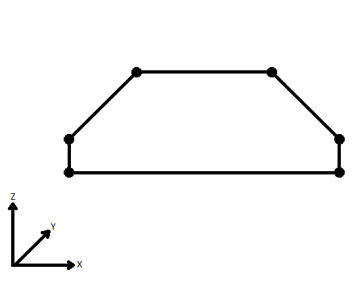
|
| Average | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is the average of the original two. |
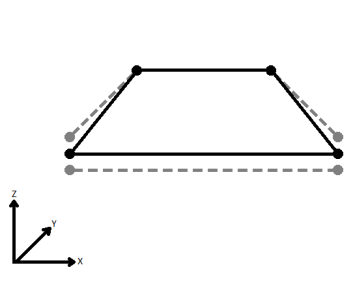
|
| First Wins | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is taken from the first encountered vertex. |
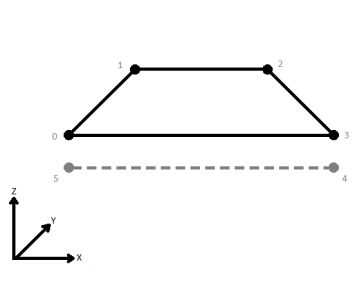
|
| Last Wins | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is taken from the last encountered vertex. |
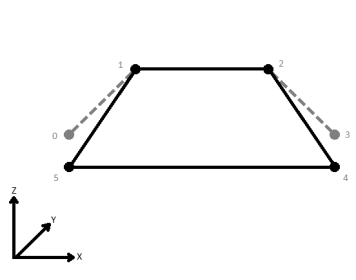
|
| Ignore | Z values are ignored. No change is made to the way the nodes are connected. |
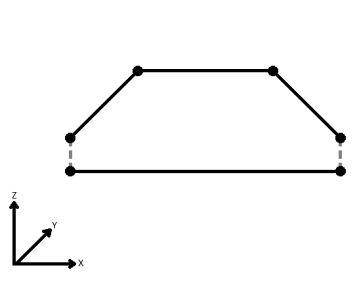
|
Choose how aggregate geometries are to be handled.
Deaggregate: Decompose aggregates into their individual components. With this setting, the transformer might output more features than were given as inputs.
Reject: Do not process aggregates and output them via the <Rejected> port.
The attribute identified by this parameter will store the number of input polygons dissolved into an output polygon.
For example, if 3 input polygons dissolved into 1 polygon, then that 1 polygon would have this attribute set to 3.
Attribute Accumulation
Specifies how attributes should be accumulated. If Drop Attributes is selected, all incoming attributes are removed from the features. Use Attributes From One Feature takes all attributes from the largest source feature. Merge Attributes merges all attributes from overlapping segments. If there are conflicts, attributes from input polygons will be preserved in a two-step process:
- First, attributes from one of the polygons with the largest area will be copied onto the output polygon.
- Second, attributes from all other input polygons will be copied, without overwrite, onto the output polygon.
Any attributes specified in this field will undergo statistical accumulation.
For example, if two input polygons have an attribute “salary” set to 30000 and 50000, then summing them would result in a “salary” of 80000 on the aggregate output.
Any attributes specified in this field will undergo statistical accumulation.
For example, if two input polygons have an attribute “salary” set to 30000 and 50000, then averaging them would result in a “salary” of 40000 on the aggregate output.
Any attributes specified in this field will undergo statistical accumulation.
For example, if two input polygons have an attribute “salary” set to 30000 and 50000, and the second polygon was 3 times larger than the first polygon, then the weighted average would be 45000.
Attributes to Average, Weighted by Area may produce non-numeric results if some input features have zero, or no area.
Generate List
This parameter specifies the name of a list into which the attributes of the input features are stored. Attributes from a feature with the largest area are stored at the head of the list, and no order is defined for the remaining elements.
For example, if 3 input polygons are dissolved into 1 polygon, then that 1 polygon would have a list with 3 entries, each containing a set of attributes from one of the 3 input polygons.
Note: List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in Workbench unless they are first processed using a transformer that operates on them, such as ListExploder or ListConcatenator. Alternatively, AttributeExposer can be used.
All Attributes: Every attribute from all input features that created an output feature will be added to the list specified in List Name.
Selected Attributes: Only the attributes specified in the Selected Attributes parameter will be added to the list specified in List Name.
The attributes to be added to the list when Add To List is Selected Attributes.
Example
The example below shows areas before and after a Dissolver transformer was used.
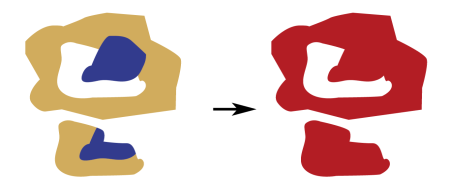
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Community.
Keywords: aggregate aggregation "technology preview"