Validates any number of attributes against user-defined test conditions, routing the feature according to the outcome of the test(s) and identifying any tests it has failed.
Typical Uses
- Performing data quality testing
-
Enforcing data integrity by testing attributes against a set of acceptable conditions
- Ensuring attributes meet the requirements of constraints and domains in output databases
How does it work?
The AttributeValidator receives features with attributes to be tested against user-defined Validation Rules.
A wide variety of Validation Rule types are available. The rules are created in a table, and each row consists of the attribute(s) to be validated, the type of test to be done, and any configuration required. An attribute may be tested against any number of rules, and a rule may be applied to any number of attributes.
There are two output ports - Passed and Failed.
Passed features are those whose attributes have passed all Validation Rule tests that have been defined.
If any tests are failed, the features will be output via the Failed port, with descriptions of the failures:
- The first test failed will be documented in the new attribute _fme_validation_message.
- The first test and any further tests failed will all be documented in the new list attribute _fme_validation_message_list{}.
Tests are evaluated in the order they are listed in the Validation Rules table in the parameters dialog.
Creating Validation Rules
Each rule consists of the attributes to be tested and the test to be performed. The following tests are available.
|
Validation Rule |
Description |
Configuration |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type |
Tests if the value is compatible with the chosen Type. You may test for multiple types by adding additional Validation Rules. |
Select the Type to test for.
|
||||||||||||||||
| In Range |
Tests if the value falls within the numeric range specified in set notation. Open-ended ranges may be defined by leaving either the lower or upper limit blank. |
Range values are separated by a comma and enclosed by brackets. Square brackets - [ ] - indicate inclusive limits (greater than or equal to, less than or equal to). Round brackets - ( ) - indicate exclusive limits (greater than, less than). Valid range examples: (1,9) Greater than 1 and less than 9 [1,9] Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 9 (1,9] Greater than 1 and less than or equal to 9 (1,) Greater than 1 [,9] Less than or equal to 9 |
||||||||||||||||
| Case | Tests if the value complies with the selected case pattern. |
Select a case pattern.
|
||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Length |
Tests if the number of characters in the value is greater than or equal to the Minimum Length. All values are evaluated as strings. |
Enter an integer. Example: If Minimum Length = 4 Bvd: Failed Blvd: Passed Boulevard: Passed |
||||||||||||||||
| Maximum Length |
Tests if the number of characters in the value is less than or equal to the Maximum Length. All values are evaluated as strings. |
Enter an integer. Example: If Maximum Length = 4 123: Passed 1234: Passed 999999: Failed |
||||||||||||||||
| In | Tests if the value may be found in provided list of possible values and ranges. |
Enter any combination of comma-separated strings, numeric values, and/or ranges (in the form of x-y). Valid configuration examples: 1,10,100 1-99 cat cat,dog,cats and dogs dogs,1-9,7 |
||||||||||||||||
| Encodable In | Tests if the value is encodable in the specified encoding without data loss. |
Select from a list of standard encodings. Sample encodings:
|
||||||||||||||||
| Not Null | Tests that the attribute exists on the feature, and is not null. | <Unused> | ||||||||||||||||
| Unique |
Tests if a value is unique (only used once) within the set of features. The first occurrence of a value will Pass, and any subsequent occurrences of that value will fail. |
<Unused> | ||||||||||||||||
| Has a Value | Tests that the attribute has a value, and is not null, missing, or empty. | <Unused> | ||||||||||||||||
| Contains Regex | Tests that the value contains a string that matches a pattern described by a Regular Expression. |
Enter a Regular Expression. The Regular Expression Editor is available via the ellipsis (...) button, and may be used to construct and test expressions. The regex to test may represent a string to be found anywhere within the value, or may represent the entire value (by creating a regex long enough to represent the extent of the desired value). Example: If regex is \d cats: Failed 9: Passed cats82: Passed |
In this example, we have a spreadsheet of food cart vendors to test for data quality.
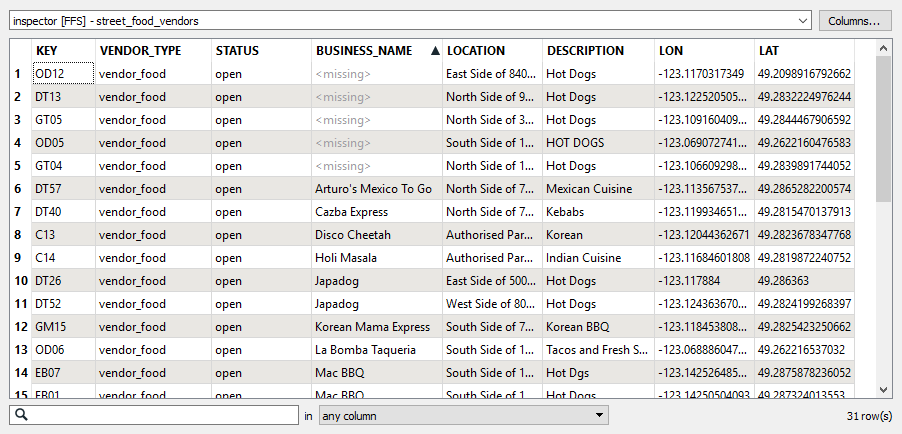
The features are routed into an AttributeValidator.

In the parameters dialog, we construct three tests to perform:
- Has a Value: All attributes are tested for the existence of any value, which will identify any missing data.
- In: The DESCRIPTION attribute is tested to see if its values are in a list of valid options. The list is typed in, with items separated by commas. Items that fail this test may have the wrong information, or data entry errors such as the wrong case or spelling.
- Type: The LAT and LON attributes are tested to see if they contain floating point numbers. As these contain the location of the vendors, items that fail this test may have invalid coordinates.

Features that fail any of the tests are output via the Failed port. A new attribute - _fme_validation_message - has been added, and contains details of the first test failed for each feature. Note that the tests are applied in the order they appear in the Validation Rule table.
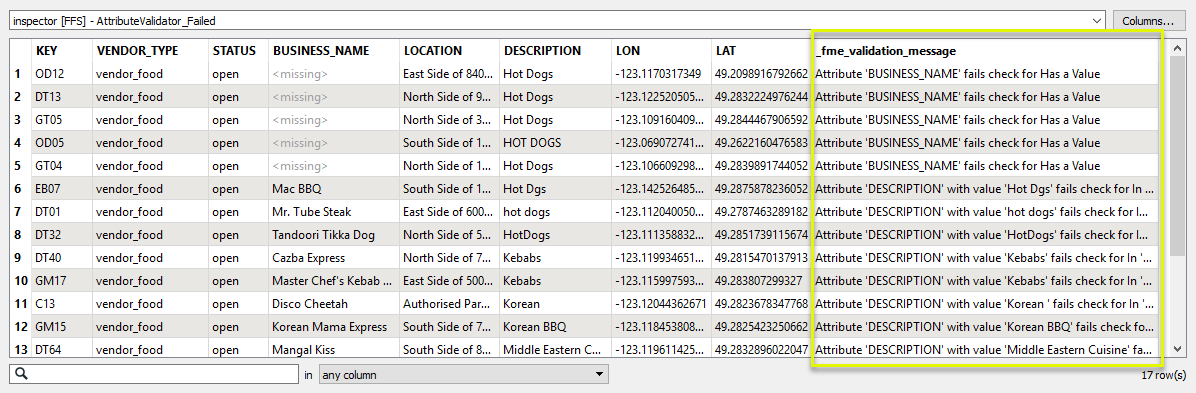
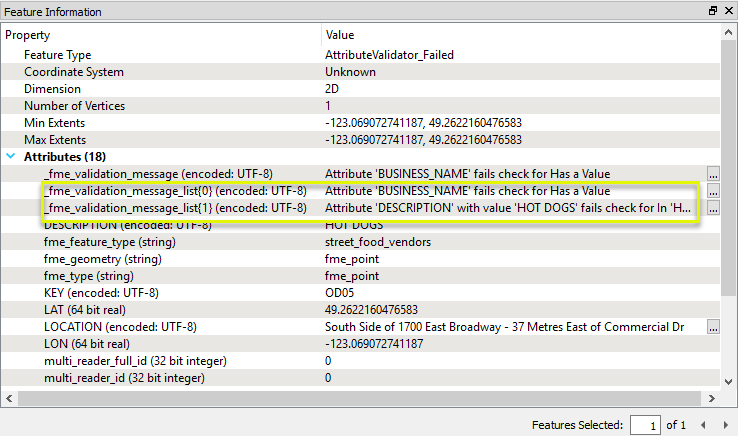
A new list attribute has also been added (which is not visible in the Table view) - _fme_validation_message_list{}. All tests failed are added to the list attribute.
Note that this feature has failed two tests - the BUSINESS_NAME does not have a value, and the DESCRIPTION has failed because the value HOT DOGS does not match the list item Hot Dogs (the case is wrong).
Configuration
Input Ports
Features with attributes to be validated.
Output Ports
If the test(s) pass, the feature is output via the Passed port.
If any test fails, the feature is output via the Failed port, with additional attributes describing the failure.
Note: Feature order may change in relation to other output ports. Feature order per port is maintained.
Parameters
See Creating Validation Rules above for further detail.
| Attributes to Validate | Select the attribute(s) to be tested. |
| Validation Rule |
Select the type of test to be performed. Options include:
|
| Rule Configuration | Enter any supplementary configuration information for the test selected. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
| A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. | |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Working with User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| FME Licensing Level | FME Base Edition and above |
| Aliases | AttributeClassifier, StringClassifier |
| History | This transformer replaced the AttributeClassifier transformer. |
| Categories |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the AttributeValidator on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver