Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Text Editor
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Arithmetic Editor
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors.
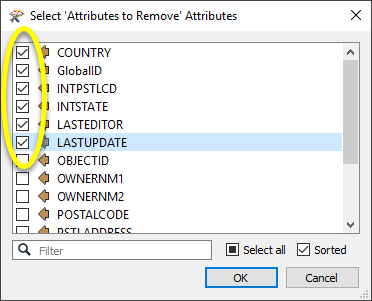
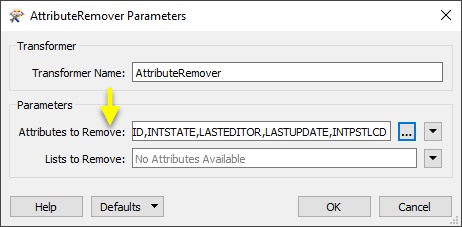
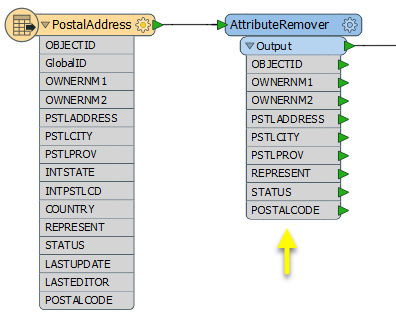
 beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see