Different feature types are read by default, depending on whether you make changes to the Reader Parameters (accessible from the Add Reader > Parameters button):
By default, all sheets and named ranges are selected. You can use the Select button to filter the display.
- When you open the Reader Parameters, by default, all of the sheets in the workbook will be selected, and all named ranges will be deselected. This is so that all cell data is read into FME only once.
- If you add a reader without opening the dialog, you will have to select which feature types to add.
Dynamic Schema
If you set Workflow Options to Dynamic Schema, then all sheets and all named ranges will be read into FME.
This option breaks the dependence on the source and destination schema. One merged feature type will be connected to one writer feature type that is configured for dynamic operation. The schema is not replicated on the workspace; therefore, if the source data changes, you will not have to update the workspace – FME will do this automatically.
This will result in duplicated data (since any information in a named range is also on the sheet that contains it), but it means that no feature types will be hidden by default.
Sheets to Read
This area shows all of the sheets and named ranges in the Excel file. A named range is of the form sheetName/NamedRangeName.
Example
In this example, the selected area is a named range: the name of the named range is date_hatched, and it is on the sheet eggs.
The column Field Names Row allows you to select which row contains the header names, and the column Cell Range allows you to restrict the information to read. If a cell in the Field Names Row is blank (if, for example, it is a merged cell), it will automatically be given the merged cell value.
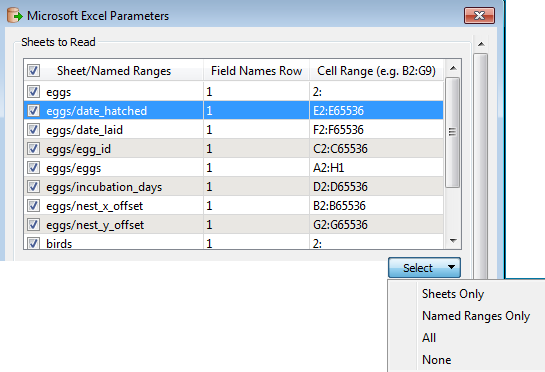
The Select menu allows you to choose which sheets/named ranges to read. By default, FME will select All.
If the column Field Names Row value is set to zero (0), then the column names will be set to the Excel column letters A, B, C, etc. This can be useful if there are no field names, or if they are not consistent.
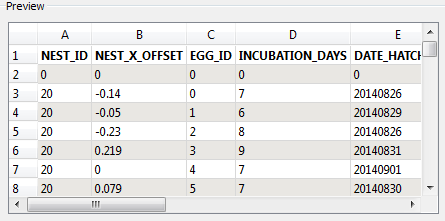
Preview
This area shows a preview of the data (up to 100 rows) of the selected feature type (either feature or named range). As shown in the example here, if you select a header row from the Sheets to Read area, that row will be shown in boldface text.
Attributes
This area displays the attributes that were created for the feature type (schema scanned).
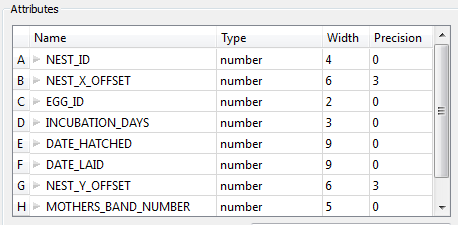
- Name: The attribute name that will be placed on resulting features.
- Type: The attribute type is listed in this column. You can change the attribute type by clicking on the field and selecting from the drop-down list. This only affects the resulting features if the selected attribute type is a coordinate type or a date type.
- Width: This value is ignored for attributes produced from this reader.
- Precision: This value is ignored for attributes produced from this reader.
|
Field Type |
Description |
|
boolean |
Boolean fields store True/False data. Data read or written from and to such fields must always have a value of either true or false. FME represents Booleans as Yes and No for True and False, respectively, so any logging within FME will reflect this. Round-tripped values will be written as True/False as expected. |
|
char(<width>) |
Character fields store fixed-length strings. The width parameter controls the maximum number of characters that can be stored by the field. No padding is required for strings shorter than this width. Notes: Strings encountered that have length greater than width will still be returned; they will not be truncated. The width parameter is only valuable if the features will be passed to another format that requires this information. |
|
datetime |
Datetime fields convert doubles or strings in Excel to FME datetime string format and are detected using the formatting value and cell value from the source file. Note that no formatting is preserved from the original value in Excel. YYYYMMDDHHmmSS.mmm (Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second, Milliseconds) |
| date |
Date fields convert doubles or strings in Excel to FME date string format, and are detected using the formatting value and cell value from the source file. Note that no formatting is preserved from the original value in Excel. YYYYMMD (Year, Month, Day) |
| time |
Time fields convert doubles or strings in Excel to FME time string format, and are detected using the formatting value and cell value from the source file. Note that no formatting is preserved from the original value in Excel. HHmmSS.mmm (Hour, Minute, Second, Milliseconds) |
|
string |
String fields store variable length character data up to a length of 32767 characters. Values larger than 32767 are truncated. |
|
number |
Number fields store single and double precision floating point values. |
|
y_coordinate z_coordinate |
Coordinate fields store double precision floating point values. There is no ability to specify the precision and width of the field. If an x and a y coordinate are specified on a feature type on read, features will use them to try to create Point geometries. The attributes are not consumed by the geometry, so they will still appear on the features produced. If your spreadsheet data contains X/Y values or Latitude/Longitude, FME automatically converts the rows to geometry. It recognizes common names for geometry columns, like “latitude” and “longitude”, allowing you to instantly visualize a spreadsheet. |
Filter
Filter a list of attributes by typing a key sequence into this field.
Read Formulas (.formula)
If this parameter is selected, an attribute will be added to the workspace for columns that contain a formula. The reader reads formulas used to calculate the values of a cell and stores the formula in the attribute <attributeName>.formula.
Read Hyperlinks (.hyperlink)
If this parameter is selected, an <attributeName>.hyperlink attribute will be added to the workspace for columns that contain a hyperlink.
Advanced
By default the Excel Reader Schema is fixed and based on the schema defined in the reader feature type. Select this parameter if you need FME to determine the schema from the current Excel file when the workspace is run.
This allows you to set up a workflow where, for example, you can edit the source Excel file without having to edit the workspace. This parameter would usually be used in conjunction with the Add Reader option Single Merged Feature Type.
When reading multiple files, only one file will be shown in the parameter dialog.
Apply default settings to additional files: The parameters in this dialog will apply only to the current file. Any additional files will use the reader’s default settings.
Apply current settings to additional files: The parameters in this dialog will apply to the any additional files. Note that any additional feature types in those files will not be picked up.
This parameter defines how FME will read back blank cells.
- Null: Blank cells will be read back as null attributes on the output feature.
- Missing: Blank cells will be read back as missing attributes on the output feature.
This parameter tells the reader what to do when it encounters a merged cell range.
- If selected (which is the default), the value will be placed into every attribute contained within the merged cell.
- If not selected, the value of the range will only be placed in the first attribute of the first attribute containing it.
For example, if there is a merged cell range of A1:B2 (which contains 4 cells) and it has the value testString:
- If you select Expand Merged Cells, you receive two features with attributes A=’testString’ and B=’testString’.
- If you do not select Expand Merged Cells, you receive one feature with attributes A=’testString’ and B=<missing> and one feature with A=<missing> and B=<missing>.
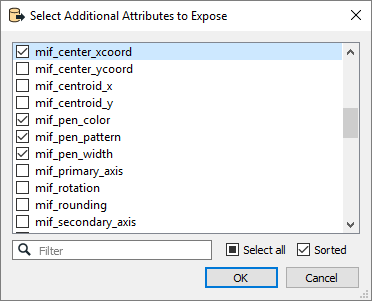
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, you can use this parameter to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types.
Additional Format Parameters (Workbench Navigator)
Some parameters are accessible only from the Workbench Navigator after you add a reader or writer to a workspace (that is, they are not visible in the reader or writer parameters dialog).
This field can be used to indicate the maximum number of rows to scan to obtain attribute types in the reader feature type. This does not affect the preview in the reader parameters, which always scans a fixed amount of rows.
If set to a value of 0, the entire file will be read to determine the schema.
See also Troubleshooting.