Understanding Feature Types and Attributes
Feature Type: the source dataset schema or structure.
Attributes: can reference either user attributes or format attributes.
About Feature Types
In FME, a Feature Type refers
to the source dataset schema or structure.
Every format used by FME identifies features through a classification
scheme. This classification is known in FME as a feature type. Feature
types are used to differentiate between different types of features (for
example roads, rivers, buildings, contours).
The feature type for any particular format
is listed in the FME Readers and Writers
manual under the "Format Quick Facts" section (see
FME Readers and Writers Reference under the Workbench help menu).
Some examples are:
- In MicroStation Design File (DGN) format, each
level is a Feature Type.
- In AutoCAD Drawing File (DWG) format, each layer
is a Feature Type.
- In Smallworld format, each class is a Feature
Type.
- In Esri Shapefile format, each file basename (*.shp
file) is a Feature Type.
A Feature Type is contained within a dataset.
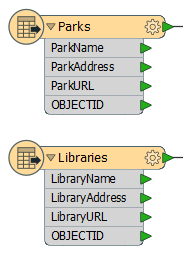
When you create a workspace using a dataset, the Feature Types present
in that dataset are shown on the left-hand side of the workspace canvas:
About User Attributes and Format Attributes
Workbench supports two types of attributes:
- User attributes
can have their names and data types adjusted to meet the needs of the
user. They correspond to the columns in any attribute tables created during
the translation.
- Format attributes
are fixed by FME. Descriptions of the attributes available for each reader
(input format) and writer (output format) are given in the FME
Readers and Writers manual. (Choose FME Readers and Writers Reference from the Workbench > Help menu.) Format attributes can be exposed
in a workspace so that they can be set to particular values.
Format Attributes
A format attribute is a built-in, FME-generated attribute that relates to the structure or symbology of a feature for any given format. For example, a format attribute records a feature’s color.
You can use these attributes to carry out certain tasks by making the attributes part of the workspace.
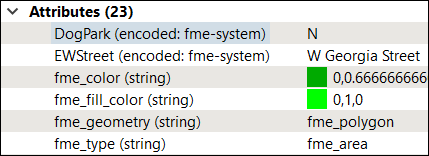
Format attributes are most visible when viewing a dataset with the Inspector (FME Data Inspector). When querying a feature, not only will user attributes be shown, but so too will format attributes. In this case, the attributes reflect the nature of the data in its source form.
More Format Attribute Examples
The color of a feature is the simplest example of a format attribute. However, there are many more, all of which vary in their degree of complexity. Some examples of format attributes include the following.
- Rotation: Many features possess a degree of rotation around the Z axis. This rotation is also stored as a format attribute; for example, fm0_rotation (the rotation of a feature in GeoMedia format).
- Subtype: For a format that supports subtypes (a sort of built-in lookup table), the value corresponding to a subtype code may be placed as a format attribute; for example, geodb_subtype_name (the subtype field for Esri Geodatabase format).
- Raster Pyramid: Raster features are handled in a slightly different way to vector features, with one of these differences being a greater reliance on format attributes. Details of Raster Pyramids are often stored or set in format attributes; for example, oracle_raster_pyramid_type (the type of pyramiding to be applied when writing raster data to an Oracle database).


