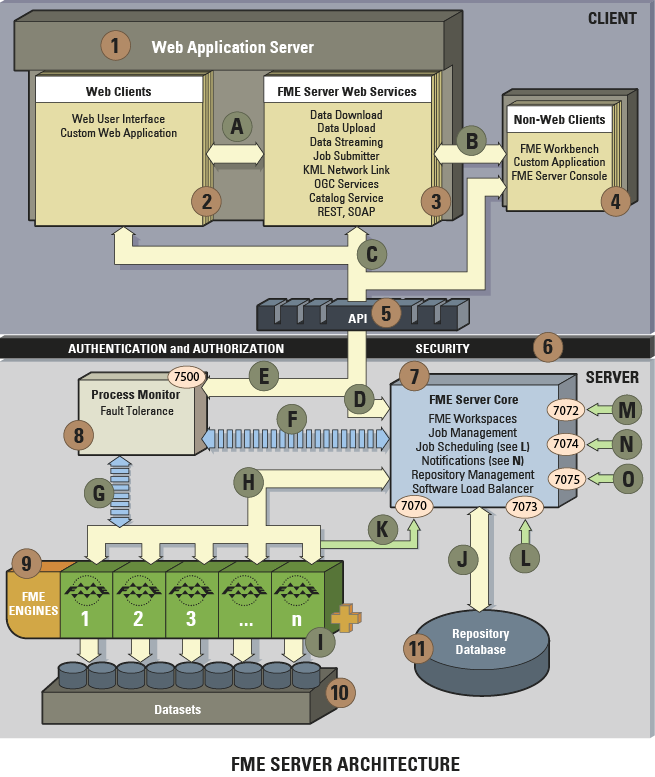
FME Server has a number of different components, some of which are considered part of the FME Server core and others that are considered clients of FME Server.
Each FME Server component is illustrated in the diagram below and described below.

FME Server Architecture
1 Web Application Server
A Java Web Application Server is required in order to run the FME Server Web Clients and FME Server Services. Supported Web Application Servers include Apache Tomcat and Oracle WebLogic.
2 Web Clients
The Web User Interface is included with FME Server and can be run in a browser:
Custom web clients can be developed on top of the FME Server REST Service. Clients can also develop against traditional Java, .NET, and C++ APIs.
3 FME Server Web Services
FME Server provides predefined services to carry out common tasks. Services provided with FME Server include:
4 Non-Web Clients
5 API
The low level FME Server API is available in Java, .NET, and C++. All requests are sent to FME Server through the FME Server API. The FME Server REST Service uses the FME Server Java API to send requests to FME Server.
6 Security
FME Server provides Authentication and Access Control using the Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) framework. FME Server also includes a security token service.
7 FME Server Core
The FME Server Core manages and distributes job requests (queuing, request routing, scheduling), the repository contents (workspaces, custom formats, custom transformers, data), and notification requests. The FME Server Core contains a Software Load Balancer (SLB) that distributes jobs to FME Engines.
8 Process Monitor
This component provides fault tolerance functionality ensuring that the FME Server Core and FME Engines remain available to process requests. The Process Monitor also provides a mechanism for managing the FME Server and FME Engine components, including the ability to start, stop, restart and add components.
9 FME Engines
FME Engines process job requests by running FME Workspaces. Each FME Engine processes a single request at a time. FME Server processing can be scaled by adding FME Engines to the same computer or to separate computers within a distributed FME Server environment.
In a distributed environment, FME Engines run on a computer or computers that are separate from the FME Server host. Administrators can configure the FME Engines to register with a failover FME Server host, which acts as a backup if the primary FME Server host fails.
10 Datasets
Typically, an FME Server job runs a workspace that reads and/or writes data. FME Server administrators must ensure that FME Engines have read access to datasets or databases the workspaces read, and write access to any directories or databases the workspaces write to.
11 Repository Database
The FME Server Core uses this database to store job and repository information. The database should never be edited directly, although querying the database for job history and other statistical information is common.
A
Web Clients use the FME Server Web Services over HTTP. Communication is defined by the Web Services API, SOAP API and REST API.
B
Non-web Clients use the FME Server Web Services over HTTP. Communication is defined by the Web Services API, SOAP API and REST API.
C
Web Clients, FME Server Web Services and non-web clients use the FME Server API to communicate over with FME Server over TCP/IP. The requests are sent to the FME Server Core over port 7071. Result messages are returned to the clients over a randomly assigned port created by the FME Server Core.
D
The FME Server API can be used to send job and repository requests to the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7071.
E
The FME Server API can be used to send Deployment Management requests to the Process Monitor over TCP/IP port 7500. The Process Monitor sends shutdown requests to the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7071.
F
The Process Monitor monitors the FME Server Core processes and restarts them if they halt. The FME Server Core also communicates with the Process Monitor over TCP/IP port 7500.
G
The Process Monitor monitors the FME Engine processes and restarts them if they halt.
H
Once registered (see K below), the FME Engines communicate with the FME Server Core over TCP/IP ports dynamically determined by the Core.
I
The FME Engines read and write data from shared/mounted drives, databases, web services, etc.
J
The FME Server Core communicates with the Repository databases via JDBC over TCP/IP.
K
The FME Engines perform initial registration with the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7070.
L
The FME Server API can be used to send job scheduling requests to the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7073.
M
The FME Server API can be used to send notification requests to the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7072.
N
The FME Subscribers (Logger, Email, HTTP Push, Apple Push Notification, FTP, Google Cloud Messaging, JMS) perform initial registration with the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7074. The FME Subscribers process notifications received by the FME Server Core.
O
The FME Publishers (Email, UDP, JMS) perform initial registration with the FME Server Core over TCP/IP port 7075. The FME Publishers relay messages to the FME Server Core.