When configured, an Apple Push subscriber can send notifications to your target app installed on an iOS device. To accomplish this scenario, the Apple Push subscriber uses the Apple Push Notification Service and two requirements from your target app, both of which require developer access:
Note: The above requirements are unique for each iOS app, and cannot be shared between different apps. When configuring the Apple Push subscriber to work with a new app, a new SSL keystore and new device tokens must be acquired.
Note: The Apple Push subscriber requires use of the outbound TCP port 2195 to send notifications. Ensure that the firewall on the FME Server host is properly configured to allow for communication using this port.
Acquiring the SSL Keystore
The SSL keystore (.p12 file) contains both a certificate and private key, and is required to establish a connection between the subscriber and the Apple Push Notification Service.
The keystore is associated with the iOS app developer, and generating the keystore is a one-time process.
The SSL keystore file and password is required when configuring the subscriber.
Acquiring the Device Token for the Target Device
Each iOS device can register itself to the Apple Push Notification Service, and when doing so, associates itself with a device token, which is a 64-digit hexadecimal number that uniquely identifies the iOS device.
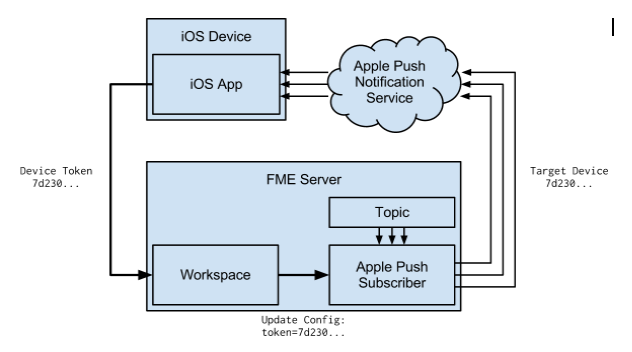
The iOS app on the device must distribute its device token to FME Server. Typically, the device token is sent to a processing workspace on FME Server that records the token and updates the subscriber. This flow is illustrated below.

An iOS app can register to the Apple Push Notification Service using method registerForRemoteNotificationTypes: , and the device token is returned in the app delegate method application:didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:. This process is described in Registering for Remote Notifications.
What's Next?